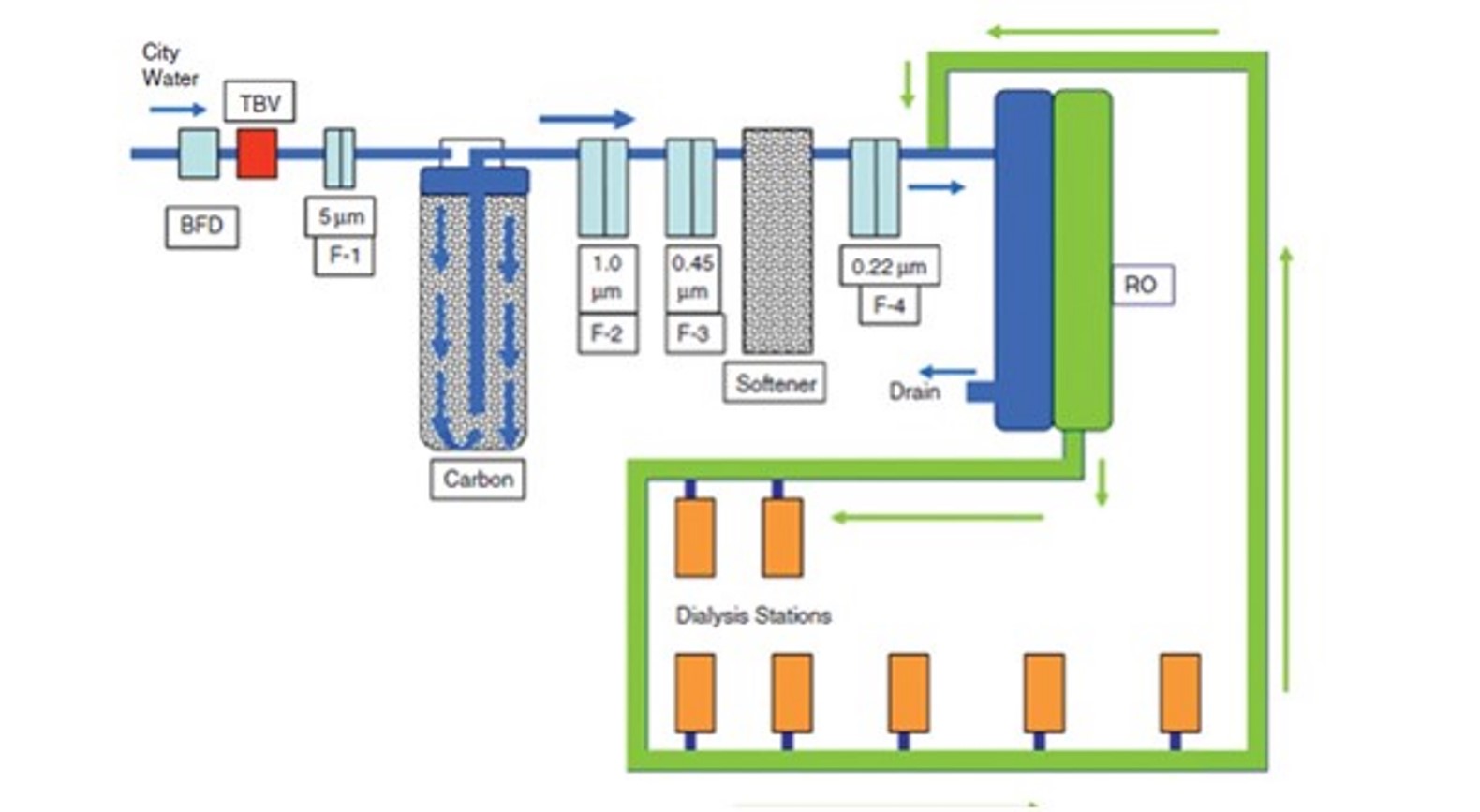
Kidney Dialysis Unit (KDU) & WFI
Ensuring the purity of water used in dialysis is paramount for patient well-being and treatment success. Several key factors underscore this importance:
Volume Exposure Discrepancy: Hemodialysis (HD) patients are exposed to a significantly larger volume of water compared to individuals with normal kidney function. While a typical person consumes around 15 liters of water per week, HD patients can be exposed to over 400 liters weekly through the dialysis process.
Protective Barriers: Unlike the natural protections afforded by the stomach acid and intestinal barrier in healthy individuals, the dialyzer membrane poses a less effective barrier against contaminants present in water.
Lack of Natural Filtration: Normally, the functioning kidneys filter out contaminants, providing an additional layer of protection for individuals with normal kidney function. However, this safeguard is absent in HD patients, necessitating stricter purity standards for dialysis water.
These considerations necessitate more stringent regulations governing the purity of water used in dialysis. Failure to adhere to these guidelines can have grave consequences for patients. The use of modern, more permeable dialyzer membranes heightens the risk of water contamination, underscoring the need for strict adherence to purity standards to prevent harm to patients.
Water authorities often add chemicals such as fluoride, aluminum, chlorine, and chloramines to enhance water quality. However, these additives can be harmful to dialysis patients as they may accumulate in the body, leading to significant morbidity and mortality. For instance, aluminum and fluoride intoxication have resulted in severe clinical complications and fatalities among dialysis patients.
Moreover, chemicals leaching from water pipes, particularly those made of lead, copper, or brass zinc, have caused chemical intoxications in dialysis patients. Therefore, it is imperative to avoid using such materials in the delivery of water for dialysis to ensure patient safety and well-being.